I. Introduction / Summary
The most practical way for a microcontroller to retrieve input is via interrupt. The vast majority of modern processors have interrupt functionality. This functionality allows a processor to work on background tasks while no input has happened. Once input is detected, the processor diverts its attention to react, then returns to where it left off after the interrupt has been serviced.
II. Description and Circuit Diagrams
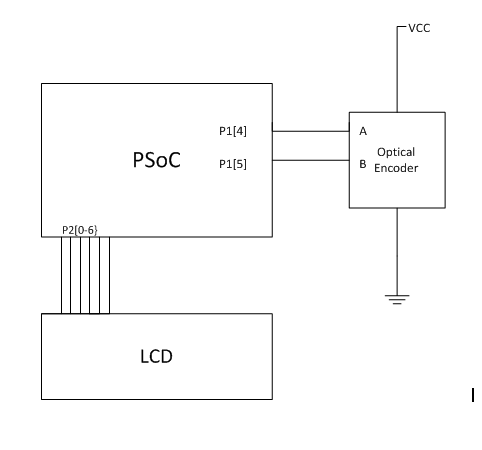
An optical encoder is connected to VCC and ground to provide power to its internal emitters, detectors, and squaring circuitry. The encoders outputs are connected to P1[4] and P1[5] on the PSoc board. P2[0-6] are connected to a LCD on the evaluation board.
Using this setup, we will display to the LCD a number between 0 and 100 that reflects the direction of the encoder rotation.
III. Description of Software
The software routine enables interrupts, starts the LCD, and takes a measurement of the B output of the rotary encoder upon startup. It then simply executes an infinite loop with no consequences. The only way to leave this loop is via an interrupt triggered by a change in either the A or B inputs from the rotary encoder. Once a change in input is detected, the execution jumps to the interrupt service routine named PSoC_GPIO_ISR_C(void). This ISR takes a measurement of the A input, clears the LCD, then performs an XOR operation on the current A and the previously stored B to determine whether the rotary encoder was turned clockwise or counter clockwise. A count variable (initially = 50) is incremented or decremented accordingly within the explicitly defined limits of 0~100. The LCD is updated to display the count variable. Finally the current value of B is stored to be used during the next execution of the ISR.
IV. Validation and Testing
The setup was tested by turning the rotary encoder clockwise and counter-clockwise while observing the LCD to see the count being updated. The encoder was moved to both the upper and lower limits to ensure that the LCD display correctly prevented any value < 0 or > 100 from being displayed.
V. Program listing
/*
* Filename: RotaryInterrupt.c
*
* Title: updating a LCD with interrupts using a rotary encoder
*
* Description: This source code file is used with a Psoc 3 microcontroller to read a rotary
* encoder. Every time the encoder is moved, the LCD is updated to reflect the movement.
*
* Copyright 2011 BK Turley & Robert Sanson. All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are
* permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
*
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of
* conditions and the following disclaimer.
*
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list
* of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials
* provided with the distribution.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY BK Turley & Robert Sanson ''AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL BK Turley, Robert Sanson OR
* CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON
* ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
* NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
* ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* The views and conclusions contained in the software and documentation are those of the
* authors and should not be interpreted as representing official policies, either expressed
* or implied, of BK Turley & Robert Sanson.
*
*/
#include <m8c.h> // part specific constants and macros
#include "PSoCAPI.h" // PSoC API definitions for all User Modules
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma interrupt_handler PSoC_GPIO_ISR_C
// Global Variables
int count = 50;
BOOL CW;
BYTE A, B;
unsigned char cnt_as_str[8];
void main(void)
{
// Enable global interrupts (see m8c.h)
M8C_EnableGInt;
// Enable GPIO Interrupts (see m8c.h)
M8C_EnableIntMask(INT_MSK0,INT_MSK0_GPIO);
LCD_Start();
// Set A and B to current values
B = OpEncB_Data_ADDR & OpEncB_MASK;
// Spin here forever
while(1);
}
void PSoC_GPIO_ISR_C(void)
{
A = OpEncA_Data_ADDR & OpEncA_MASK; // get current A value
LCD_Control(LCD_DISP_CLEAR_HOME); //clear lcd
CW = (B >> 5) ^ (A >> 4); //determine CW or CCW
if (CW)
{
if (count <= 99)
count++;
} else {
if (count >= 1)
count--;
}
//display count on line 1
itoa(cnt_as_str,count,10);
LCD_Position(0,0);
LCD_PrString(cnt_as_str);
B = OpEncB_Data_ADDR & OpEncB_MASK; //get fresh value for B
}